Learn about Pine64's boards and modules, including the PINE A64, which hails as a replacement for Raspberry Pi 3.
The first Pine A64 boards, claiming to be a replacement for the Raspberry Pi 3, were successfully crowdfunded in 2016. Since then, the Pine64 family has grown to include a variety of boards and products and boasts an active forum.
The Rock64 and SOPINE A64 add more options for users. Though all three board families have configurable features, we will be focusing on the Pine A64-LTS, RockPro64, and Sopine A64 as they are the newest version of each board. We’ll also take a look at a couple of other products by Pine64, including the Pinebook and the PADI IoT Stamp.
Getting Started with Pine64 Boards
The PINE A64-LTS and SOPINE A64 utilize the SOPINE OS, while the ROCKPro64 utilizes the Pine64 OS, available on GitHub. Peripherals available include the Wifi/BT module, a camera module and a 7” LCD panel.
The PINE A64-LTS, ROCKPro64, and SOPINE A64 currently all have a long-term supply service through 2022.
The PINE A64-LTS Single Board Computer
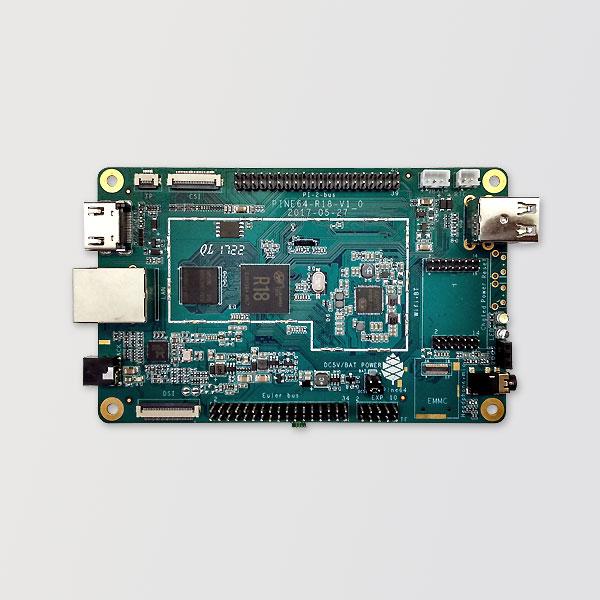
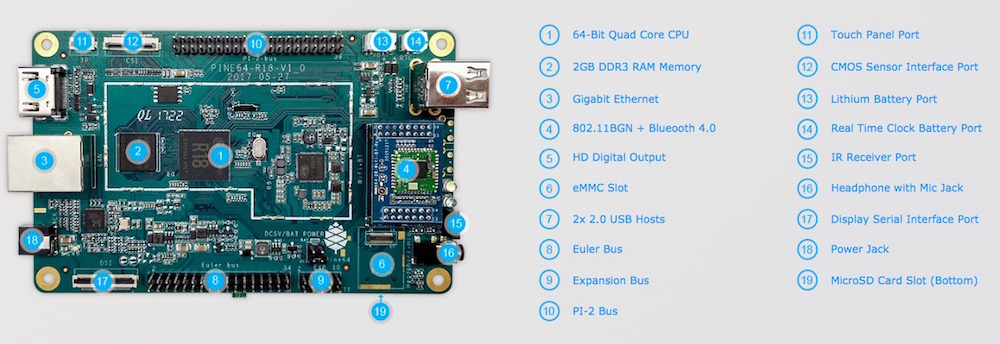
The Pine A64-LTS is the long-term supply version of the Pine64 board. This single board computer (SBC) is powered by an Allwinner R18 quad-core ARM Cortex A53 64-bit processor. It comes with 2GB of LPDDR3 memory and 128Mb of SPI boot flash, along with support for an eMMC module (up to 128GB) and microSD booting.
An overview of the PINE A64-LTS board. Image courtesy of Pine64.
Features
- PI-2 GPIO Bus
- Euler GPIO Bus
- UART, SPI, I2C interfaces
- USB 2.0 port (x2)
- Real Time Clock
- IR receiver port
Because of the memory configuration, this board uses Sopine OS builds instead of Pine A64+ OS builds.
The SOPINE A64: A Computing Module
The SOPINE A64 is a small compute module powered by the same Quad-Core ARM Cortex A53 64-Bit Processor used in the PINE A64.
An overview of the SOPINE 64-bit computer module. Image courtesy of Pine64.
Features
- 2G LPDDR3 RAM memory
- power management unit
- SPI flash
- MicroSD Slot (for bootable OS images microSD card)
With a SODIMM-DDR3 form factor commonly found in notebook computers, users can incorporate multiple SOPINE A64s into their projects to increase computing power.
To turn the SOPINE A64 into an SBC, makers can purchase the SOPINE Baseboard “Model A” separately. The Baseboard “Model A” helps with early development stages.
The ROCKPro 64
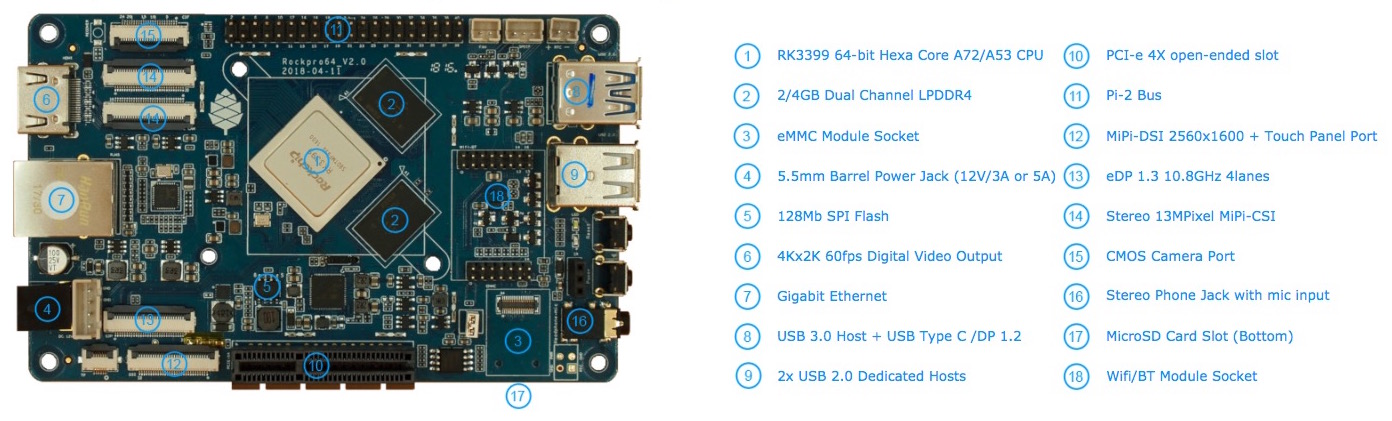
The 64-bit Hexa-Core RockPro64 is Pine64’s most powerful SBC.
An overview of the ROCKPro64 SBC. Image courtesy of Pine64.
There are two ROCKPro64 boards available: one with 2GB of dual-channel LPDDR4 system memory and one with 4GB. Currently, the 4GB version is listed as LTS and the 2GB version is not.
Features
- USB 3.0 port
- USB type C with DP1.2 port
- PCIe 4x open-ended slot
- eMMC module socket
- 40-pin header with I2C, SPI, UART, and GPIO
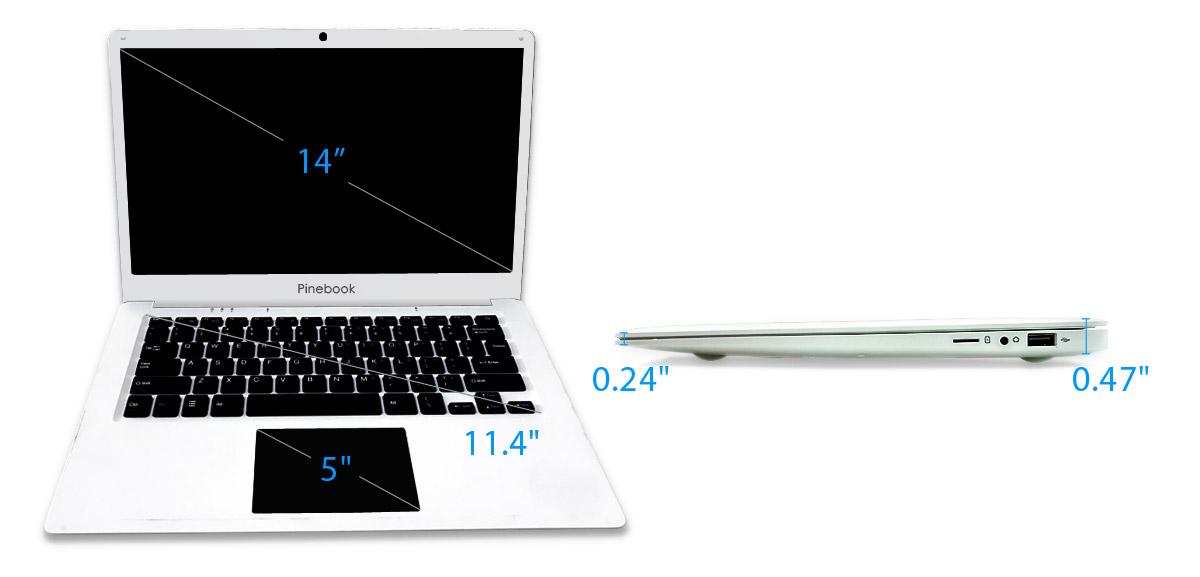
The Pinebook
The Pinebook is a 64-bit open source notebook that uses the same Quad-Core ARM Cortex A53 64-Bit Processor used in the Pine A64. It comes with 2GB of RAM, 16-64GB of eMMC 5.0 flash, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth 4.0 capabilities.
The Pinebook. Image courtesy of Pine64.
Features
- Full-sized keyboard and touchpad
- .3MP camera
- built-in microphone
- USB 2.0 port (x2)
- microSD slot
- Headphone jack
- Digital video port
The hardware for this budget computer may not be impressive—in fact, on PINE64’s website there is a disclaimer that this is NOT a replacement for a more traditional laptop—but it can run some Linux distributions as well as Android.
PADI IoT Stamp
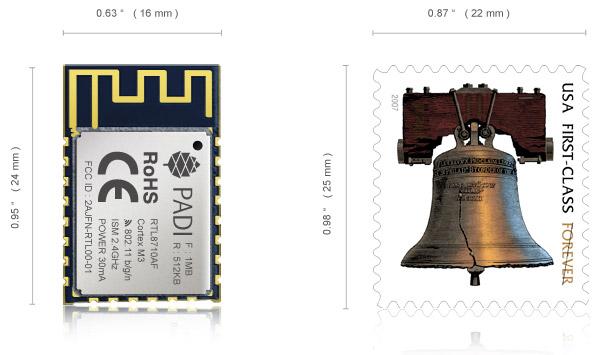
For IoT applications, the PADI Wi-Fi controller features a built-in antenna, ARM Cortex M3, integrated Flash and RAM, WLAN MAC, WLAN baseband, RF balun, PA, LNA receiver, saw filter and power management module.
The PADI IoT Stamp compared to a US postage stamp. Image courtesy of Pine64.
The 83MHz ARM Cortex M3 takes advantage of 1MB of ROM, 512KB of RAM, and 1MB of flash memory. It includes different interfaces like SPI(1), UART(3),I2C(1), GPIO(19), as well as 4 PWM pins.
As for software, the PADI Stamp is compatible with the WPA/WPA2 security standards using WEP,TKIP, and AES encryption. Firmware can be updated through UART, OTA, or JTAG using IAR, openOCD, or J-Link.