-
Categories
-
Platforms
-
Content
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Scroll to continue with content
Arouse1973
Adam
Just out of interest why do you think is not a PWM circuit?
Thanks
Adam
Thanks
Adam
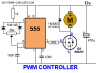
This is the one i use for PWM circuit testing.
http://www.discovercircuits.com/DJ-Circuits/simplepwm2.htm
M.
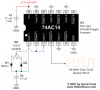
http://www.discovercircuits.com/DJ-Circuits/simplepwm2.htm
M.
Arouse1973
Adam
Who says the frequency has to be constant for it to be PWM?Because pwm relies on a fixed frequency adjustable duty cycle.. these change the frequency, there's no pulse width change, just frequency modulation
Adam
Who says the frequency has to be constant for it to be PWM?
Adam
Pretty much everyone.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pulse-width_modulation
ak
Arouse1973
Adam
Yeah everyone but me then
Adam
Well, I don't know who or what defines PWM, but I looked at this link and I don't think it comes down that clearly in favour of fixed frequency.
In 2.6 they say there are 3 types of PWM, all of which are based on a fixed frequency. That might imply they (whoever they are) do think PWM must be based on fixed frequency, but I can't spot anywhere that they state this.
On the other hand in 21. 1nd 2.2 they do talk very briefly about delta and delta-sigma modulation. Now I must admit that these are normally generated using a fixed frequency clock, but I can't see any reason why this is necessary. The output waveform from the modulator certainly doesn't look like a fixed frequency PWM. The shortest pulse is one clock period, but the longest can be many clock periods. As far as the demodulator is concerned, any clock frequency is irrelevant and could be varied, or even varying, quite significantly without making any difference to the output.
In 3.5 they talk about class D amplification. Again here, I guess, fixed frequency is the norm, but I can't see that fixed frequency is necessary in any way.
In both these cases I'm not sure whether they are correct in calling these PWM, as I see them more as pulse density modulation. So maybe fixed frequency could be a way of distinguishing between genuine PWM and primitive PDM, which is actually an analogue modulation which just looks like a digital signal.
Well, I don't know who or what defines PWM...
I do.
There is no standards organization or regulating body for modulation schemes. Like the Smith Chart and S-parameters, these are industry standard terms, developed and refined over decades, and taught in curricula as a part of the baseline information necessary to function in the field of electrical engineering.
PWM - Pulse Width Modulation - the width of the pulse is modulated as a function of an input signal. Not the amplitude (PAM), not the frequency (PFM), and not the timing (PPM); only the width. Very common in switching power supplies, including LED dimers and digital audio power amps.
PFM - Pulse Frequency Modulation - the rate of occurrence of a pulse (its frequency) is modulated as a function of an input signal. The pulse width is a constant, and there is a varying time between pulses. Used in Vicor high-density switching power supply DC/DC converters.
PAM - Pulse Amplitude Modulation - the amplitude of a pulse is modulated as a function of an input signal. Not the width, and not the frequency. An early form of telephone signal multiplexing.
PPM - Pulse Position Modulation - the position of a pulse within a defined time frame is modulated as a function of an input signal. Pulse width and amplitude are constant. Used in deep-space probes and R/C airplanes.
Each of these has a Wikipedia page.
One way to differentiate (and define) modulation schemes is by their output power spectral densities with equal modulating input signals. As above, there is no industry-wide standard for this, although some industry segments (such as telecom or datacom) have developed standard measurement environments and evaluation criteria.
ak
Last edited:
??? I'm not gunning anyone. I always try to go beyond the minimum tech answer and provide some context to help make the answer more clear or more useful. Pointing out that the answer is thousands of years old, isn't gunning, but I can see where it might be taken that way. Never my intent, even with Colin.
OTOH, new/young people ask questions, which is why we're all here, and by definition they all are not well-formed. If you (not you-cj, but you-anyone) can't answer an honest question without berating or beating up someone, wear a cup.
ak
OTOH, new/young people ask questions, which is why we're all here, and by definition they all are not well-formed. If you (not you-cj, but you-anyone) can't answer an honest question without berating or beating up someone, wear a cup.
ak
When i'm bored i'll have read up on those
When I'm bored, I answer questions on engineering fora.
ak
Similar threads
- Replies
- 22
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 11
- Views
- 10K