This project describes the definition and the location of a car fuse box as well as some signs of a blown fuse.
In this project, you will know some basic vehicle electrical problems, particularly in the Blown Fuses. It is very essential to tell the blown fuses.
What is Fuse Box?
What's the difference between an electrical panel and a fuse box? To many non-electricians, they may sound the same, and they are frequently discussed as if they were interchangeable. They aren't, and knowing the difference is important if you live in an older home with an outdated version.
Fuse boxes are designed to protect electrical circuits in vehicles from damage and short circuits caused by exposure to the elements. Fuses are designed to control and protect electrical currents flowing through wires to electrical components. When fuses blow, drivers may experience problems with the radio, dome lights, and other electrical components in the vehicle. While you may suspect that a blown fuse is to blame for a loss in electrical mechanisms, it is entirely possible that your battery or alternator is to blame. When multiple fuses blow, the fuse box is most likely experiencing a problem. When one or more of your vehicle's electrical components fail, car fuse box service may be required.
If your vehicle lacked fuses, an overloaded electrical current could cause the wiring to overheat, melting the insulation and starting a fire. Any electrical mechanism that receives a large current will fail immediately. Fuses stabilize currents, allowing the mechanism to operate without interruption. On rare occasions, the current may be too great for even the fuse, causing it to blow. If you are having trouble starting your vehicle or are unable to operate your headlights, windshield wipers, interior lights, radio, or other electrical components, a fuse may have blown.
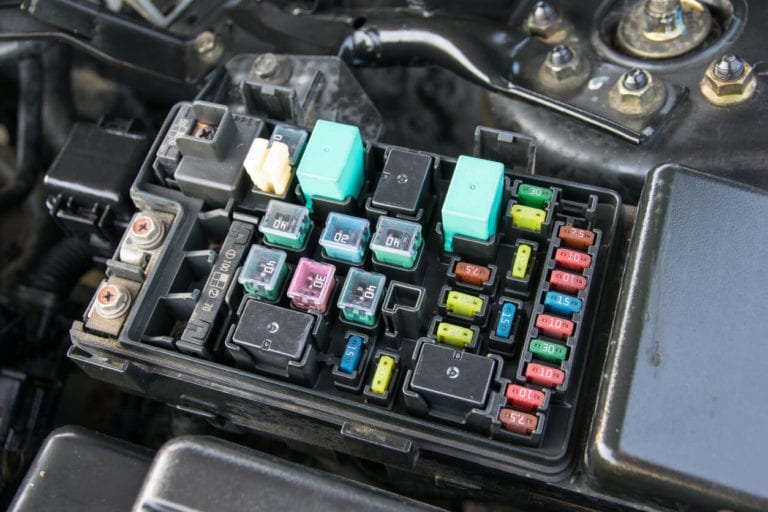
The Fuse Box Location
Fuse boxes in vehicles can be found in a variety of locations. The location of the fuse box in a car can be found in the owner's manual. Many vehicles have two fuse boxes, which are usually located in the engine compartment as well as beneath or within the dashboard. Each box serves a distinct function. The engine compartment fuse box is designed to protect engine components such as the anti-lock brake pump, engine control unit, and cooling system, whereas the interior fuse box is used to protect electrical elements in the cabin. Fuse boxes house multiple fuses and relays for a variety of functions in one location for convenience and protection against damage caused by weather or collisions.
Fuses in the fuse box come in a variety of shapes, colors, and sizes. They are used to stabilize the electrical current flowing through wires, thereby protecting electronics from damage caused by an electrical overload. The majority of fuses in today's vehicles are rectangular or cylinder in shape. Rectangular fuses have two push-in connectors connected by fuse wiring that is protected by a plastic cover and will blow if overloaded. Cylinder fuses resemble fluorescent light bulbs in appearance. Each end has a protective housing with glass in between. When the metal ends are overloaded, a thin fuse wire, protected by the glass, burns through and blows.
While a blown fuse is most likely to blame for a single electrical issue, multiple electrical issues could be the result of a faulty wiring harness or a malfunction in the vehicle's internal computer. Your next step should be to seek the advice of a trained professional. For example, when the fuse box clicks and the car won't start, a relay is frequently to blame due to a failure from the vehicle's computer, problems with the ground wire on the control side of the relay, or a problem with the power supply to the control area of the relay. It is difficult to determine the cause and will necessitate the use of a technician's scan tool.
Electrical problems in vehicles that aren't caused by the alternator or battery are most likely the result of a melted fuse that disrupts the flow of electricity. In some cases, a blown fuse is simply a symptom of a larger problem; fuses frequently blow due to age and usage, or drivers and passengers have overloaded the vehicle's accessories. Furthermore, fuses blow when they are used at the incorrect amperage or are of poor quality. Replace a 10-amp fuse with a 30-amp fuse if possible. The 10-amp is intended to blow at a lower current rate, whereas the 30-amp allows for a higher current to pass through. A higher current passing through an area designed only for lower currents may cause component damage.
Fuses are the electrical mechanisms of your vehicle's protectors. Relays in the fuse box protect passengers from the high voltage generated by the battery and alternator. The fuse box is intended to protect the fuses and relays from damage caused by weather, water, and other driving situations. Car fuse boxes can fail due to overheating for a variety of reasons, including the addition of electrical accessories or components that produce overloaded currents.
Symptoms of a Bad or Failing Fuse Box
1. Fuses blow frequently
Fuse blowing frequently is one of the first signs of a fuse box problem. If the fuse box has any wiring issues, such as a short, the fuses may blow frequently. The vehicle may repeatedly blow the same fuse for no apparent reason. To determine if this is the problem, the fuse box may need to be disassembled or removed.
2. Loose fuses
Loose fuses are another sign of a bad or failing fuse box. If any of the fuses fall out or come loose easily, this could indicate that some of the panel's terminals are damaged. A damaged terminal with a blown fuse can cause electrical problems like sudden, intermittent power outages to specific accessories or lights.
3. Burned fuses or terminals
Burned fuses or terminals are another, more serious symptom of a fuse box problem. If the terminals or fuses become overheated for any reason, they may burn up. The terminals or the plastic that makes up the housing may become burned or melted, necessitating the replacement of the panel and, in some cases, rewiring.
While many fuse boxes are designed to last the life of the vehicle, they can develop problems and require service. If your vehicle exhibits any of the above symptoms, or you suspect that your fuse box needs to be replaced, have it inspected by a professional technician such as one from YourMechanic, to determine if the fuse box should be replaced.