This article introduces commonly-used fuses and discusses their uses in a variety of circuits.
Fuses protect circuits from current surges, making them critical components in electronics. Current surges can cause dielectric breakdown in transistors and capacitors, overheat components till they melt, or just cause weird behavior in your completed circuit. Fuses come in many different shapes and sizes and any half-decent engineer always includes one on a commercial product.
SMD Fuses
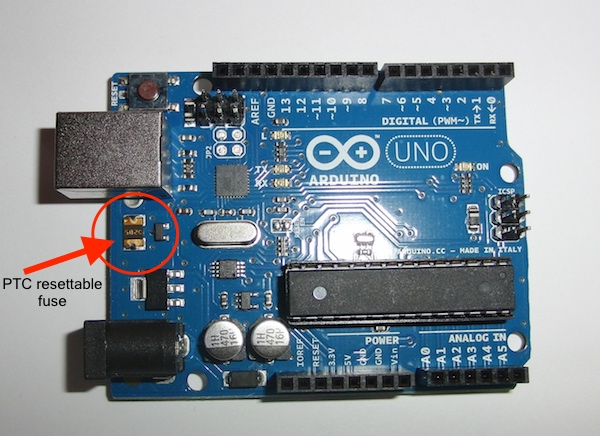
There are many types of fuses in a variety of different packages, but the SMD fuse is arguably the most common electronic fuse found on PCBs. While these fuses can have different colors and identifiers they are often large (as compared to other surface mount components), and have the component legend symbol F or FUSE. SMD fuses are often resettable which means when the fuse “blows” it can be reused after some time.
An SMD fuse on the Arduino UNO.
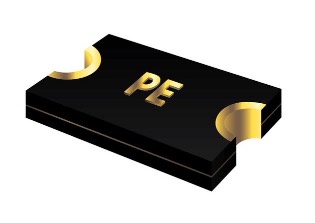
An SMD fuse. Image courtesy of Mouser.
Through-Hole Fuses
Through-hole fuses are capable of handling more current than SMD fuses and come in both resettable and non-resettable varieties.
Resettable through-hole fuses are most often disc shaped and yellow but they can be found in square packages.
A resettable disc fuse (left) and a resettable square fuse (right). Images courtesy of Mouser.
Through-hole fuses with glass bodies are always non-resettable as they consist of a thin piece of wire inside an inert gas that melts during a current surge. Through-hole fuses may have their trip current printed on their surface. If they don’t, they should have a part number available that can be used to identify the fuse type.
Through-hole glass fuses. Image courtesy of Mouser.
Glass Fuses
Glass fuses are available in through-hole packages (as pictured above) but the non-leaded types are more common—they can found on PCBs, consumer units, and even mains plugs! This type of fuse is inserted into a fuse holder which could be either through-hole, SMD, or a screw fit part allowing for the easy replacement of non-resettable fuses. These fuses will either have their fuse rating on the body (where the glass is wrapped in a paper covering), or on the metal contact ends.
Automotive Fuses
Automotive fuses are another common type of fuse found in cars, vans, trucks, and even ride-on mini tractors! These fuses consist of a pair of metal contacts that have a piece of fuse wire between the contacts and are hot-swappable, so they’re very easy to change.
Automotive fuses. Image courtesy of Mouser.
It is easy to determine if the fuse is blown because automotive fuses are transparent. The top of the fuse has the fuse rating printed on it. These fuses do come in different sizes (such as micro fuses) but their shape remains the same.