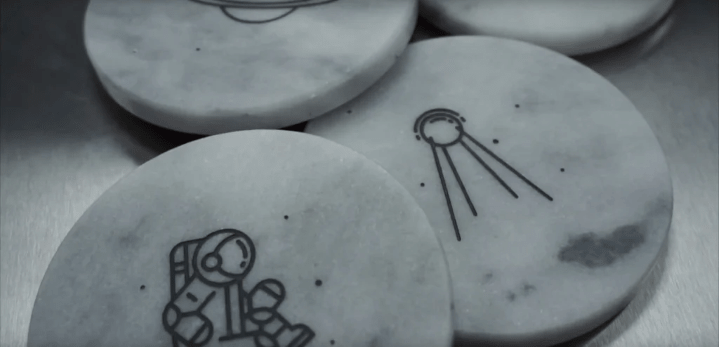In this part of this series on prototyping, learn all about laser cutting, another way to bring your designs to life!
Yet another technology for translating digital designs into physical prototypes is laser cutting. Like 3D printing and CNC machining, laser cutting uses a computer-controlled machine to create prototype parts.
Laser cutters cut parts from sheets of material using a laser powerful enough to ablate the material and create very fine cuts. Almost all laser cutters can also perform engraving in addition to cutting by reducing the laser’s power.
The video below from Glowforge shows a pour-over coffee maker made out of several different materials cut out on a laser cutter.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting fills a specific niche among the other prototyping technologies discussed in this series. The most unique aspect of using laser cutting for prototyping is the fact that laser cutters can only work with sheets of material. Depending upon the power of the laser itself, laser cutters can work with a wide range of materials, but all the materials are sheets of varying thickness.
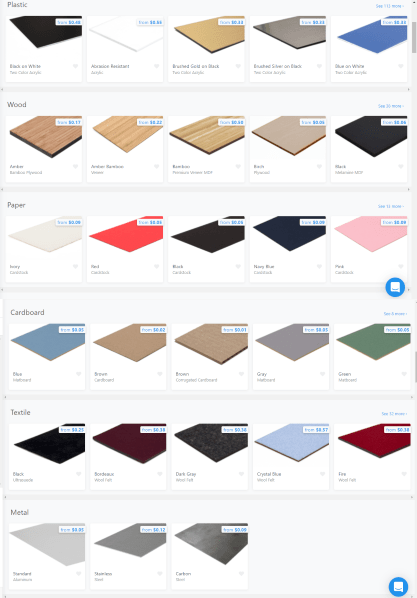
This is a selection of materials available from a laser cutting service called Ponoko
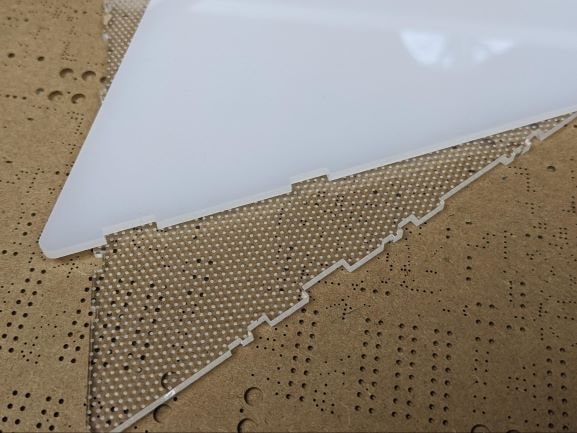
For certain types of prototypes, cutting and engraving sheets of material produces parts that work well without any assembly or post-processing. For example, laser-cut acrylic works extremely well as a light diffuser for LED projects. These laser-cut light-diffusing pieces can be used for low-volume manufacturing or to prototype parts that will be manufactured via injection molding.
This is an LED diffuser made from laser-cut clear acrylic. The part’s periphery was cut with the laser and the small dots covering the part were engraved into the material
Laser Cutters for Highly Detailed Designs
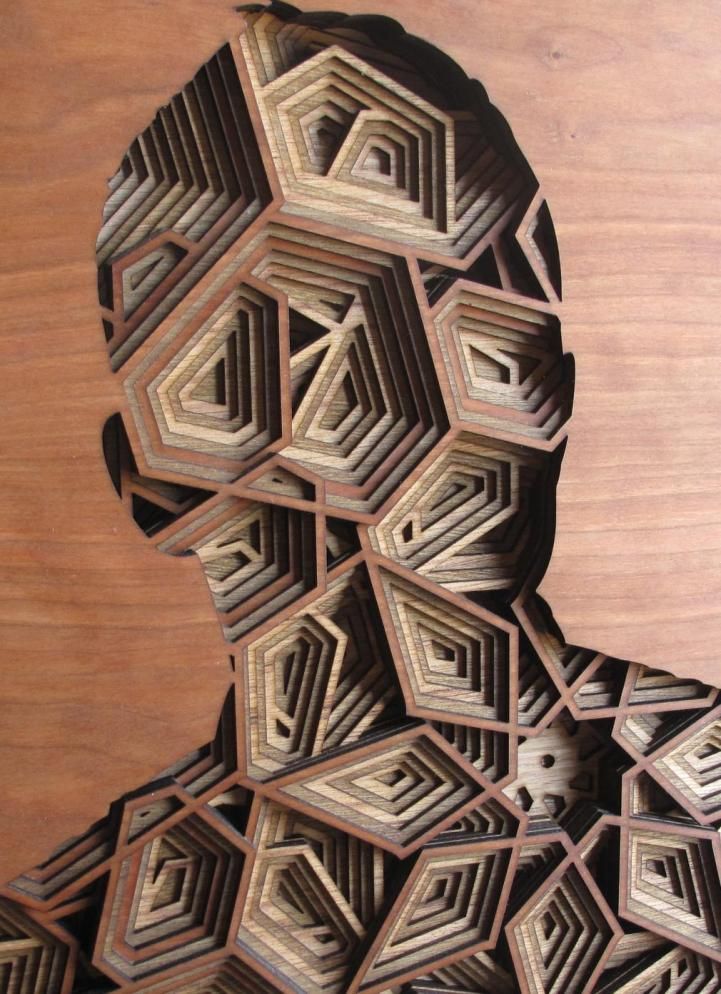
Owing to the extremely high level of detail laser cutters are capable of delivering, the technology is also often used for artistic products and for bespoke, custom-designed or customized products.
Laser cutters can cut very intricate designs from a variety of materials. They can also engrave highly-detailed designs into materials or other products to create things like custom-engraved electronic devices.
Laser cutters can produce extremely intricate designs
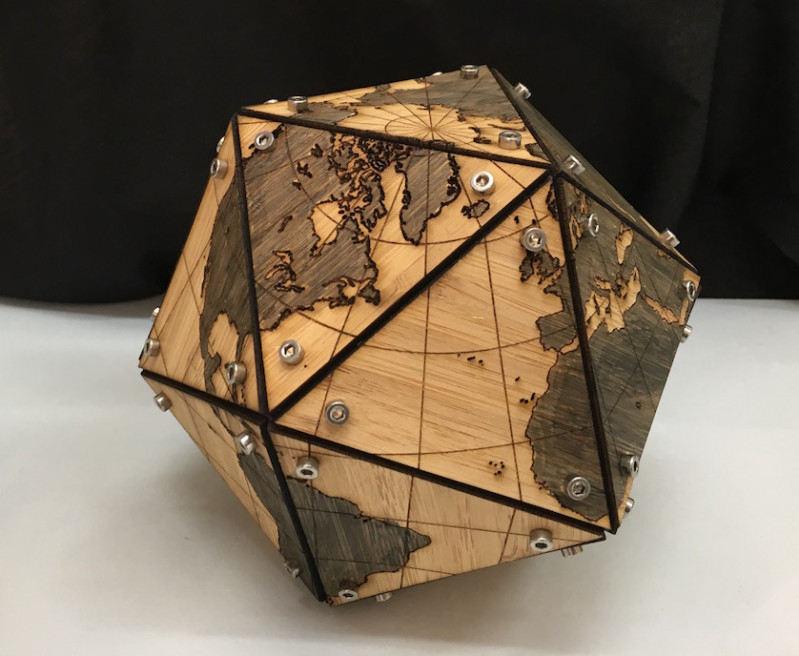
Although laser cutting only produces flat parts, the technology can be used to create parts that assemble into three-dimensional structures. For example, many early 3D printers were built from laser-cut wood that slotted together to create the printer frames.
This is the Printrbot Jr. made from interlocking laser cut wooden parts
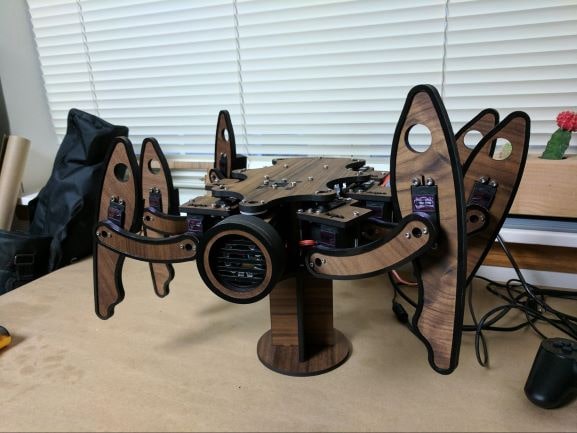
Laser cut parts can, of course, also be combined using other hardware, like simple screws, nuts, and brackets to create more complex structures.
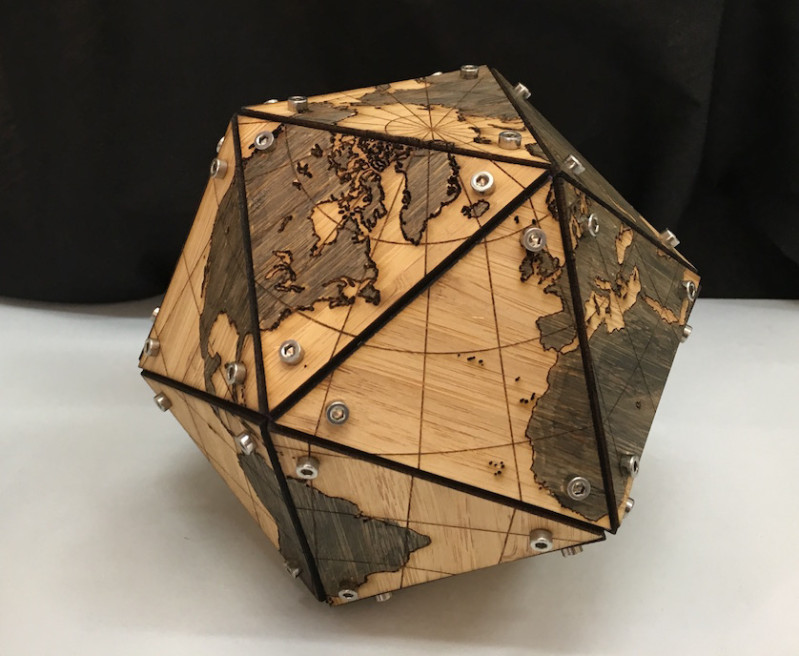
This robot is made from laser cut wooden panels joined together with various other hardware and servo motors.
Advantages of Prototyping Designs With Laser Cutting
Laser cutting, like the other technologies discussed in this article so far, has some advantages and some disadvantages for designers prototyping their products.
The most significant advantage of laser cutting over 3D printing or laser cutting is the high level of precision the technology offers. Laser cutting and laser engraving can achieve extremely intricate details in prototype parts.
In these “Lixie” displays, laser-engraved acrylic is edge lit from the bottom to create illuminated numbers.
Along the same lines, unlike CNC machining, in which designers must take the diameter of the cutting tool into consideration while designing a part, the "diameter" of the laser beam, called the kurf, is small enough that it can be, for most designs, ignored.
Laser cutters are capable of producing parts with right-angle corners anywhere in the design.
Because the laser beam itself is extremely thin, laser cutters are able to create right-angle inside corners and extremely precise engraving
Another benefit to using laser cutting for prototyping is the wide range of materials available. For solid materials, the selection for laser cutters is not quite as large as for CNC machines, but it is much greater than the material selection for 3D printers. Laser cutters can make parts from acrylic (plexiglass), various types of wood, cardboard, delrin, cork, aluminum, stainless steel, PETG, styrene, MDF, and many others.
Because laser cutters do not make physical contact with workpieces during cutting and engraving, they can also make pieces from materials that cannot be used on a CNC machine. These include soft materials like leather, paper, felt, silicone rubber, many types of fabric, and even foods.
Last, for some materials that can only be cut on an extremely powerful industrial laser cutter, engraving is still possible using laser cutters accessible to makers like glass, marble, titanium, ceramic, stone, and Corian.
Laser cutters cannot cut marble, but they can be used to engrave it.
Disadvantages of Laser Cutting Prototypes
Materials selection and cutting technology are also key downsides to laser cutting. Although the selection of material types is extensive, laser cutting technology requires that all these materials be in thin sheets. Depending upon the type of material and the power rating of the laser, materials can be used that are up to 6mm thick. Laser cutters, unlike CNC machines, are only capable of cutting straight through materials. They cannot be used to create blind holes or cavities.
As far as accessibility goes, laser cutting is in between 3D printing and CNC machining. An entry-level laser cutter is certainly more expensive than an entry-level 3D printer. However, laser cutters are easier to use than CNC machines; they are closer to being plug-and-play like prosumer 3D printers. This way of use extends to the software used to prepare files for laser cutting as well. Design files can be created in almost any vector drawing software like Adobe Illustrator or Inkscape.
Design files for laser cutters can be created using software like Adobe Illustrator
Unlike 3D printers though, some infrastructure is required for using laser cutters. Because of the way laser cutters vaporize material to cut it, the machines produce noxious, sometimes toxic, fumes. Therefore, laser cutters need to be either vented outside or their exhaust passed through a HEPA filter.
Final Thoughts on Laser Cutters for Prototyping
Laser cutting is similar in many ways to CNC milling. Both technologies use computer-guided cutting tools to make parts from sheets of material. CNC machining uses mechanical cutting tools, whereas laser cutters use powerful lasers to cut parts from a wide range of materials.
Laser cutting excels in creating parts with very fine details or right-angle corners. Laser cutters are also capable of engraving intricate designs onto a range of different materials.
Laser cutting can produce parts with extremely fine details. Laser cutters are also capable of engraving detailed designs onto parts