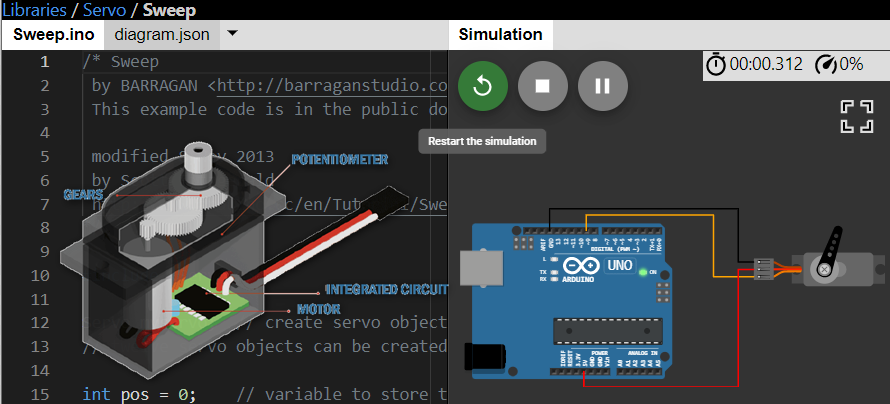
This project demonstrates the code for servo motor sweep example on virtual Arduino simulator from wokwi.
Servo motor basics
Servo motors are very much user-friendly compared to other motors. The programming is easy. The software drivers are easily available.
The Servo motors consist of a small intelligent comparator inside which can be programmed using a PWM signal. The angle of rotation is controlled by the pulse width oh the PWM signal. What this means is, even if there is a slight offset in the rotation angle (due to the load or due to a small shock) it will be corrected sooner. This Servo motor feature makes it a good candidate for several applications such as robotic arms, dispensers and more.
Servo motor element in Virtual Arduino Simulator
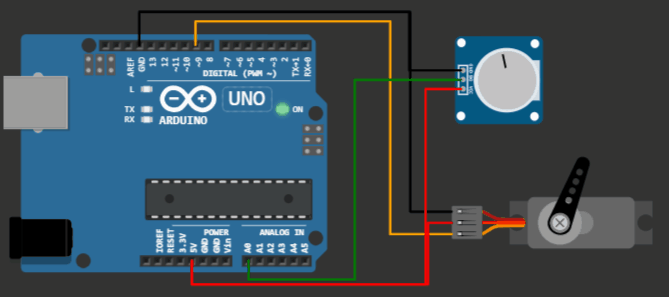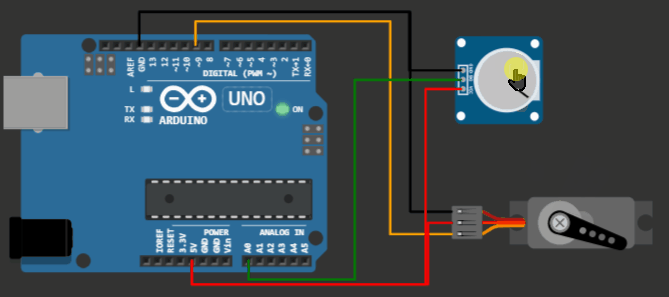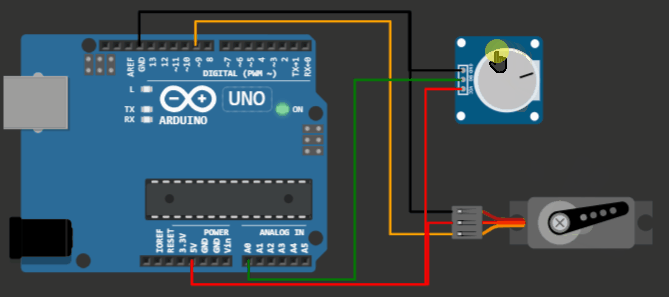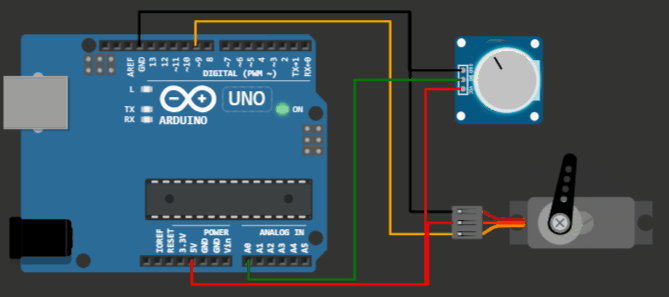
Project 1: Knob code example for Servo motor on Virtual Arduino Simulator
Servo motor Arduino project - knob example
/*
Controlling a servo position using a potentiometer (variable resistor)
by Michal Rinott <http://people.interaction-ivrea.it/m.rinott>
modified on 8 Nov 2013
by Scott Fitzgerald
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Knob
*/
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
int potpin = 0; // analog pin used to connect the potentiometer
int val; // variable to read the value from the analog pin
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
val = analogRead(potpin); // reads the value of the potentiometer (value between 0 and 1023)
val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 180); // scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180)
myservo.write(val); // sets the servo position according to the scaled value
delay(15); // waits for the servo to get there
}
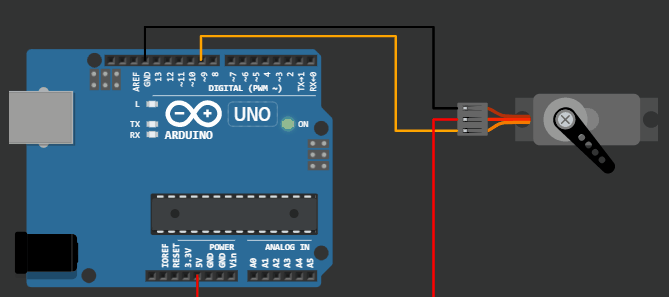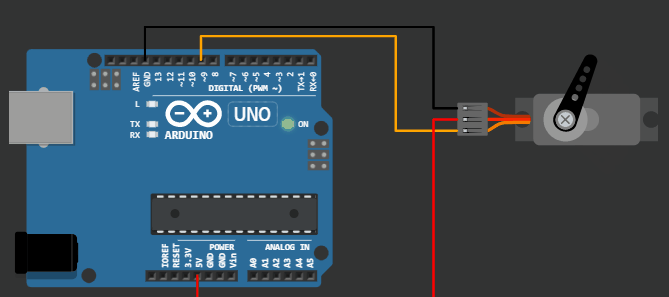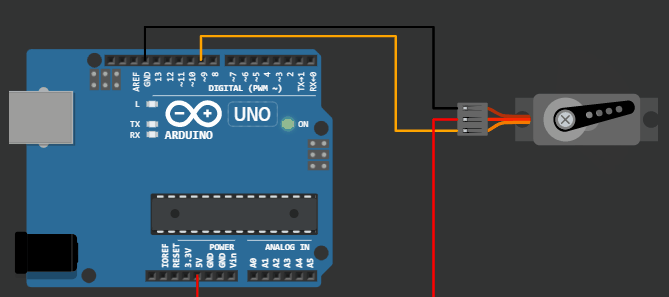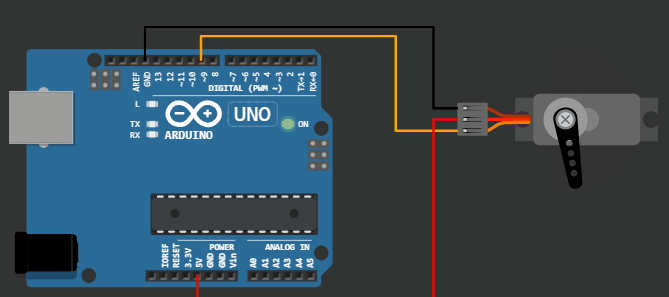
Project 2: Sweep example for Servo motor
Wokwi Arduino Simulator example = Servo motor 180-degree sweep
/* Sweep
by BARRAGAN <http://barraganstudio.com>
This example code is in the public domain.
modified 8 Nov 2013
by Scott Fitzgerald
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Sweep
*/
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
// twelve servo objects can be created on most boards
int pos = 0; // variable to store the servo position
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
for (pos = 0; pos <= 180; pos += 1) { // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees
// in steps of 1 degree
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
for (pos = 180; pos >= 0; pos -= 1) { // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
}
You can tinker with the code for the project above here
More about virtual Arduino online simulator from Wokwi