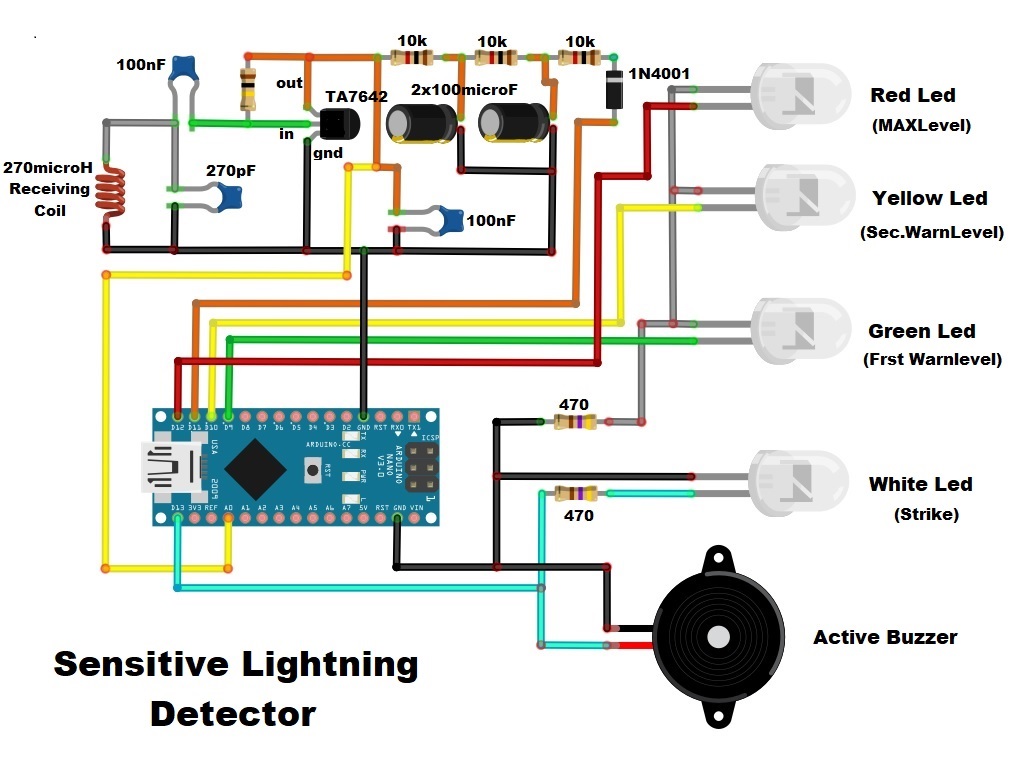
How to make a Sensitive homemade Lightning detector based on cheap AM Receiver IC TA7642 and Arduino Nano
A lightning detector is a device that detects lightning produced by thunderstorms.
In one of my previous videos, I showed you how to make such a detector with the help of the AS3935 sensor board which is specially designed for this purpose. This time I will show you how to make same such device, but now with a homemade detector circuit based on cheap AM Receiver IC TA7642.
This design is many times cheaper, its sensitivity is much higher, and Also the resistance to local disturbances as various sparks from electrical devices is very high. The ingenious idea of using AM receiver IC as a detector is presented on elektronik-labor.de page under the name "The Franzis thunderstorm warner". The basic Arduino code is taken from Ramser-elektro, and I modified it by adding an active Buzzer and some other small changes.
The device is relatively simple to build and contains several parts:
- Arduino Nano microcontroller
- four LEDs for a visual indication with resistors
- active buzzer as an audio indicator
- and small galvanometer also for visual indication
The detector works in the following way: The radio waves from the lightning are received, pre-amplified, demodulated and amplified by the TA7642. Then the output is routed to the analog input A0 of the Arduino. This results in a "voltage drop" in the voltage at the A0 Arduino input per lightning discharge. The more "voltage drops" at the analog input, the more discharges, the closer the thunderstorm.
The sensitivity of the device as well as the resistance to disturbance can be changed in the following two lines of code:
PWM_DutyCycle = (PWM_DutyCycle /3 ) * 2; // PWM value is set to 2/3, for more sensivity 5/6 or 8/9
if (Difference> = 15) { // Would test 12 times there.
The way the device works is: When starting, the voltage of the TA7642 is increased until a certain basic voltage is applied. This is indicated by turning on all the LEDs one by one and finally when all are turned off the device is ready for detection. We perform a thunder simulation with a piezo lighter. The device detects the spark from the piezo lighter at a distance of 1 meter and more. In real conditions, depending on the strength of the lightning, the range reaches up to hundred kilometers. Electrical discharge detection is indicated by a flashing white LED and a short beep from the piezo booster. There is also a small analog instrument whose arrow deflects with each lightning strike.
If a certain number of electrical discharges occur per unit time, the green LED starts flashing and this is the first level of warning. This means that the storm is close to our region. If the discharges continue, the yellow LED starts flashing, which indicates the second level of warning, and the storm is gradually approaching. Finally, if the red LED flashes, a third level warning is activated, which means that our region is hit by a storm. By reducing the frequency of electrical discharges, the warning level is automatically reduced.
The device is installed in a suitable box made of PVC with a thickness of 5 mm, which is coated with colored wallpaper.
// Firmware for Blitz-o-shield Rev.1
// Firmwareversion: Rev.0
// Copyright F.R. 2019
// www.ramser-elektro.at
//
//
#include <Wire.h>
const bool SendFullDebugText = true; // Send debug message over RS232?
const word RemoteImpulseTime = 000; // Set how long the remote impulse will be
int LED_red = 12;
int LED_yellow = 10;
int LED_green = 9;
int LED_strike = 13;
int PWM_pin = 11;
int REMOTE_pin = 7;
int AnalogIn = A0;
word ActValue; // Actual value of analog signal
float AverageValue; // Averange value
int Difference; // Difference value (AverageValue - ActValue)
word StrikeCount; // Actual strikecounter. Every strike 32 is added.
word WarnLevel = 255; // Actual warning level
word Decay; // Value, how much the warnlevel is decreased, if no activity
word InactivityTimer; // Timer for new PWM tune, if no activity
bool Blink; // Helper for LED blinking
unsigned long PreviousRemoteMillis = 0; // Helper for remote impulse
word PWM_DutyCycle; // Actual duty cycle for PWM
word PWM_Duty_Watchdog; // Helper for PWM Adjustment
unsigned long PreviousMillis = 0; // Helper for 1 second cycle
void setup(){ // Assign the hardware setup
pinMode(LED_red, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED_yellow, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED_green, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED_strike, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWM_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(REMOTE_pin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
analogReference(INTERNAL); // Set the reference voltage to 1.1 volt
TunePWM();
}
void TunePWM(){ // Setup the PWM and tune it
if (SendFullDebugText){
Serial.print("PWM duty cycle tuning started");
Serial.print("\r\n");
}
PWM_DutyCycle = 0; // First discharge the capaciators
analogWrite(PWM_pin,PWM_DutyCycle);
digitalWrite(LED_green, HIGH); // Set green LED = capaciator discharged
delay(250);
ActValue = analogRead(AnalogIn); // Read dummy
PWM_Duty_Watchdog = 0; // Reset watchdog
while (ActValue < 1023){ // Has analogue input reached the maximum?
ActValue = analogRead(AnalogIn); // Read analog input
AverageValue = ActValue; // Preset avarange value
PWM_DutyCycle = PWM_DutyCycle +1; // Increase PWM level
PWM_Duty_Watchdog = PWM_Duty_Watchdog +1; // Increase the PWM watchdog
analogWrite(PWM_pin,PWM_DutyCycle);
delay(250); // Always wait a little time, to load the capacitors
if (ActValue > 341){ // Set yellow LED = ActValue > 1/3 of maximum.
digitalWrite(LED_yellow, HIGH);
}
if (ActValue > 682){ // Set red LED = ActValue > 2/3 of maximum.
digitalWrite(LED_red, HIGH);
}
if (PWM_Duty_Watchdog >= 255){ // Maximum PWM duty cycle reached. Something is wrong!!
Blink = !Blink; // LED Blink Helper
if (SendFullDebugText){
Serial.print("Problem while adjust PWM Duty cycle. Maximum reached!!!");
Serial.print("\r\n");
}
digitalWrite(LED_green, Blink); // Blink all LED in endless loop
digitalWrite(LED_yellow, Blink);
digitalWrite(LED_red, Blink);
digitalWrite(LED_strike, Blink);
delay(500);
}
ActValue = analogRead(AnalogIn); // Read analog input
AverageValue = ActValue; // Preset avarange value
}
PWM_DutyCycle = (PWM_DutyCycle /3 ) * 2;
analogWrite(PWM_pin,PWM_DutyCycle);
digitalWrite(LED_strike, HIGH); // Set white LED = Tune PWM successful
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(LED_green, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_yellow, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_red, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_strike, LOW);
if (SendFullDebugText){
Serial.print("PWM duty cycle tune successfull");
Serial.print("\r\n");
}
}
void loop(){
ActValue = analogRead(AnalogIn); // Read in actual value
AverageValue = AverageValue * 15; // Calculate the averange value
AverageValue = AverageValue + ActValue;
AverageValue = AverageValue / 16;
Difference = AverageValue - ActValue;
if (Difference >= 15){ // STRIKE !!!
digitalWrite(LED_strike, HIGH);
delay(50);
digitalWrite(REMOTE_pin, HIGH); // Set remote action
PreviousRemoteMillis = millis();
StrikeCount = StrikeCount + 32;
if (StrikeCount >= 255){ // More then 8 Strikes in 1 Second ?
StrikeCount = 255; // More then 8 strikes per second don't happen naturaly
}
}
else{
digitalWrite(LED_strike, LOW);
}
if ((millis() - PreviousRemoteMillis >= RemoteImpulseTime) and (digitalRead(REMOTE_pin))){ // Remote impulse time elapsed
digitalWrite(REMOTE_pin, LOW);
}
if (millis() - PreviousMillis >= 1000){ // 1 Second elapsed
Blink = !Blink; // LED Blink Helper
if (StrikeCount > 32){ // At leased 2 strikes in one second
WarnLevel = WarnLevel + StrikeCount; // Increase Warnlevel
}
Decay = highByte(WarnLevel);
WarnLevel = WarnLevel - Decay; // Level decreasing
if (WarnLevel < 1000){ // No LED on
digitalWrite(LED_green, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_yellow, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_red, LOW);
}
if ((WarnLevel >= 1000) and (WarnLevel < 1500)){ // Green LED on
digitalWrite(LED_green, Blink);
digitalWrite(LED_yellow, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_red, LOW);
}
if ((WarnLevel >= 1500) and (WarnLevel < 2500)){ // Yellow LED on
digitalWrite(LED_green, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_yellow, Blink);
digitalWrite(LED_red, LOW);
}
if (WarnLevel >= 2500){ // Red LED on
digitalWrite(LED_green, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_yellow, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED_red, Blink);
}
if (WarnLevel >= 3000){ // Maximum reached
WarnLevel = 30000;
}
if (SendFullDebugText == true){ // Send debugmessage over RS232
// PWM;ActValue;AverangeValue;Difference;Warnlevel;Decay;Strikecount;
Serial.print("PWM:");
Serial.print(PWM_DutyCycle);
Serial.print(" Actual:");
Serial.print(ActValue);
Serial.print(" Averange:");
Serial.print(AverageValue);
Serial.print(" Difference:");
Serial.print(Difference);
Serial.print(" Warnlevel:");
Serial.print(WarnLevel);
Serial.print(" Decay:");
Serial.print(Decay);
Serial.print(" Strikecount:");
Serial.print(StrikeCount);
Serial.print("\r\n");
}
if (Decay == 0){ // No activity. Increase InactivityTimer
InactivityTimer = InactivityTimer +1;
if (InactivityTimer >= 3600){ // No activity for one hour. Tune PWM.
TunePWM();
InactivityTimer = 0;
}
}
StrikeCount = 0; // Reset strikecounter
PreviousMillis = millis(); // Save actual millis, for the next 1 second cycle
}
}