In this project, we are going to interface the Gravity Infrared CO2 Sensor with Arduino to estimate the CO2 concentration in PPM.
Summary
In this project, we are going to interface the Gravity Infrared CO2 Sensor with Arduino to estimate the CO2 concentration in PPM.
About Project
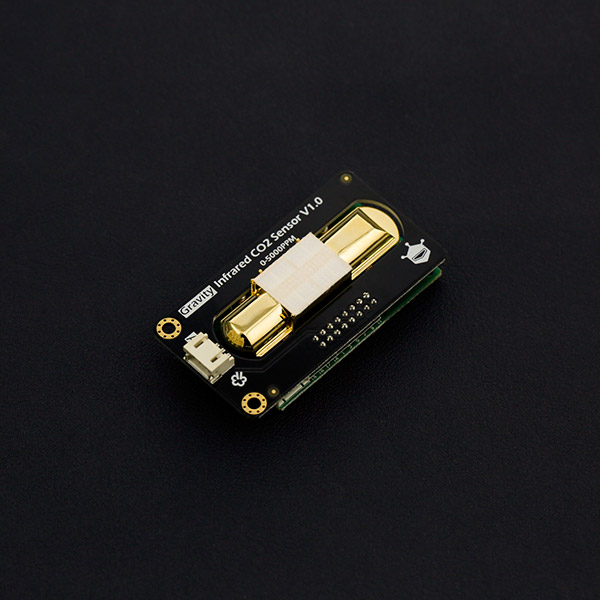
Gravity Infrared CO2 Sensor
Gravity Infrared CO2 Sensor is the current high-precision analog infrared CO2 sensor. The Infrared CO2 Sensor basically comes with a 3-pin connector. This sensor is based on non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) technology and has better selectivity and oxygen-free dependency. It combines temperature compensation and assists DAC output.
The efficient measuring range of this sensor is from 0 to 5000ppm with an accuracy of ± 50ppm + 3%. This Infrared CO2 Sensor can be utilized in HVAC, indoor air quality analyzing, industrial process as well as security protection analyzing, agriculture as well as animal husbandry production process analyzing.
OLED is a self-light-emitting technology, designed by placing a series of organic thin films in between two conductors.
int sensorIn = A4;
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 128 // OLED display width, in pixels
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64 // OLED display height, in pixels
// Declaration for SSD1306 display connected using software SPI (default case):
#define OLED_MOSI 9
#define OLED_CLK 10
#define OLED_DC 11
#define OLED_CS 12
#define OLED_RESET 13
Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT,
OLED_MOSI, OLED_CLK, OLED_DC, OLED_RESET, OLED_CS);
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set the default voltage of the reference voltage
analogReference(DEFAULT);
display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC);
display.clearDisplay();
display.display();
}
void loop(){
//Read voltage
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorIn);
// The analog signal is converted to a voltage
float voltage = sensorValue*(5000/1024.0);
if(voltage == 0)
{
Serial.println("Fault");
}
else if(voltage < 400)
{
Serial.println("preheating");
}
else
{
int voltage_diference=voltage-400;
float concentration=voltage_diference*50.0/16.0;
// Print Voltage
Serial.print("voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.println("mv");
//Print CO2 concentration
Serial.print("CO2 Concentration: ");
Serial.print(concentration);
Serial.println("ppm");
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(WHITE);
display.setCursor(18,43);
display.println("CO2");
display.setCursor(63,43);
display.println("(PPM)");
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(28,5);
display.println(concentration);
display.display();
display.clearDisplay();
}
delay(2000);
}