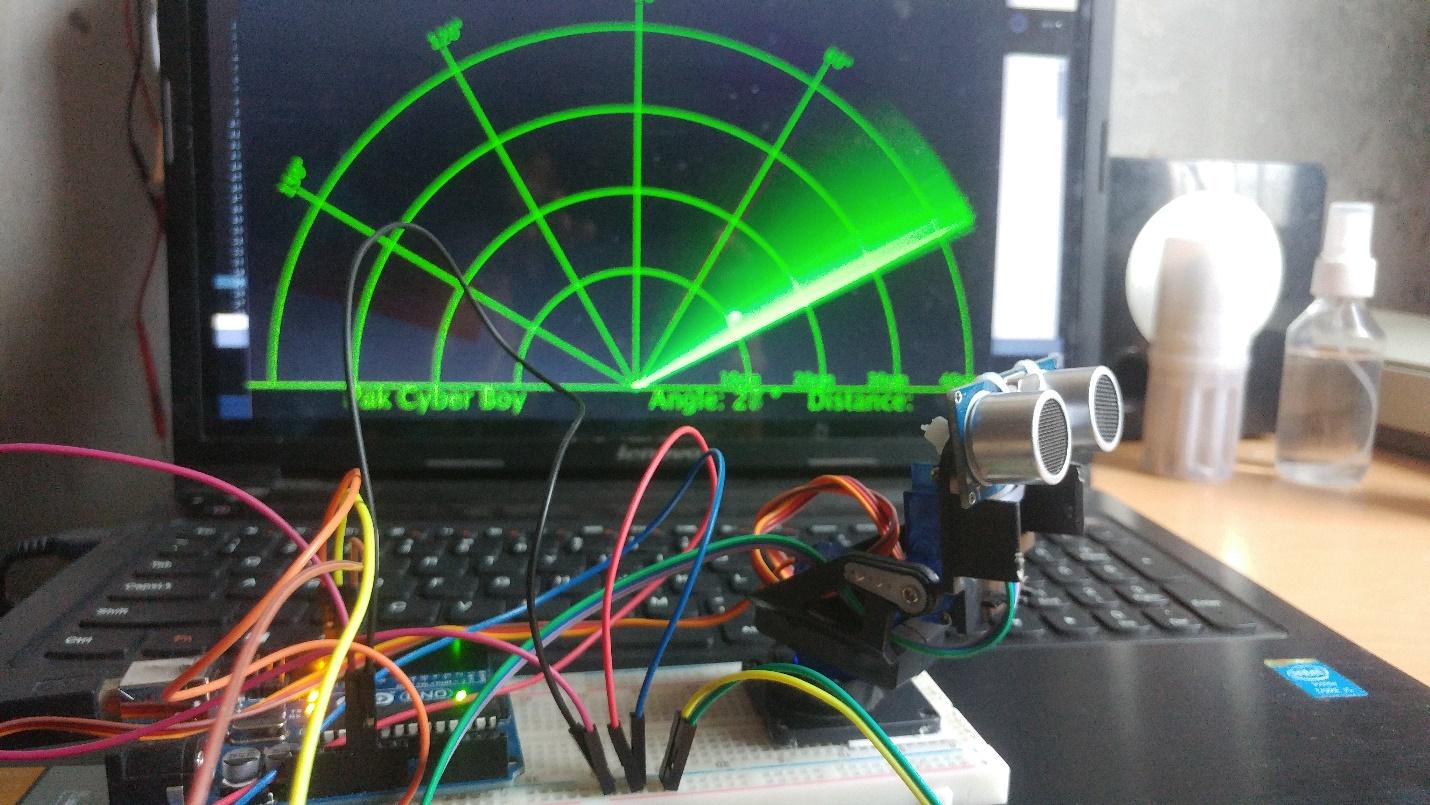
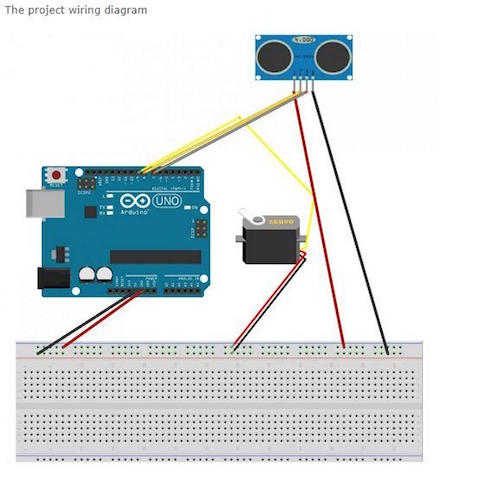
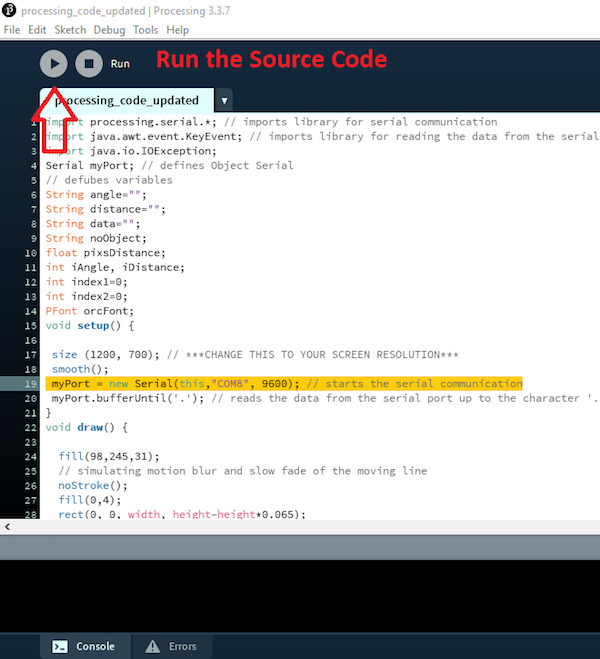
import processing.serial.*; // imports library for serial communication
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent; // imports library for reading the data from the serial port
import java.io.IOException;
Serial myPort; // defines Object Serial
// defubes variables
String angle="";
String distance="";
String data="";
String noObject;
float pixsDistance;
int iAngle, iDistance;
int index1=0;
int index2=0;
PFont orcFont;
void setup() {
size (1200, 700); // ***CHANGE THIS TO YOUR SCREEN RESOLUTION***
smooth();
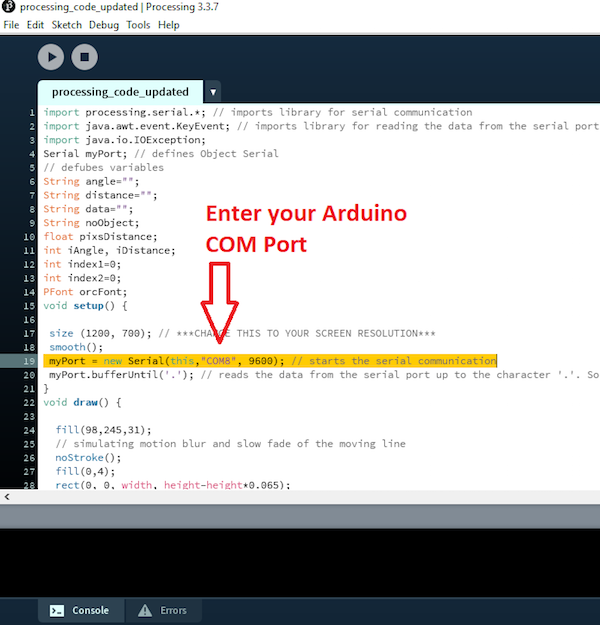
myPort = new Serial(this,"COM8", 9600); // starts the serial communication
myPort.bufferUntil('.'); // reads the data from the serial port up to the character '.'. So actually it reads this: angle,distance.
}
void draw() {
fill(98,245,31);
// simulating motion blur and slow fade of the moving line
noStroke();
fill(0,4);
rect(0, 0, width, height-height*0.065);
fill(98,245,31); // green color
// calls the functions for drawing the radar
drawRadar();
drawLine();
drawObject();
drawText();
}
void serialEvent (Serial myPort) { // starts reading data from the Serial Port
// reads the data from the Serial Port up to the character '.' and puts it into the String variable "data".
data = myPort.readStringUntil('.');
data = data.substring(0,data.length()-1);
index1 = data.indexOf(","); // find the character ',' and puts it into the variable "index1"
angle= data.substring(0, index1); // read the data from position "0" to position of the variable index1 or thats the value of the angle the Arduino Board sent into the Serial Port
distance= data.substring(index1+1, data.length()); // read the data from position "index1" to the end of the data pr thats the value of the distance
// converts the String variables into Integer
iAngle = int(angle);
iDistance = int(distance);
}
void drawRadar() {
pushMatrix();
translate(width/2,height-height*0.074); // moves the starting coordinats to new location
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(98,245,31);
// draws the arc lines
arc(0,0,(width-width*0.0625),(width-width*0.0625),PI,TWO_PI);
arc(0,0,(width-width*0.27),(width-width*0.27),PI,TWO_PI);
arc(0,0,(width-width*0.479),(width-width*0.479),PI,TWO_PI);
arc(0,0,(width-width*0.687),(width-width*0.687),PI,TWO_PI);
// draws the angle lines
line(-width/2,0,width/2,0);
line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(30)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(30)));
line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(60)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(60)));
line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(90)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(90)));
line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(120)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(120)));
line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(150)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(150)));
line((-width/2)*cos(radians(30)),0,width/2,0);
popMatrix();
}
void drawObject() {
pushMatrix();
translate(width/2,height-height*0.074); // moves the starting coordinats to new location
strokeWeight(9);
stroke(255,10,10); // red color
pixsDistance = iDistance*((height-height*0.1666)*0.025); // covers the distance from the sensor from cm to pixels
// limiting the range to 40 cms
if(iDistance<40){
// draws the object according to the angle and the distance
line(pixsDistance*cos(radians(iAngle)),-pixsDistance*sin(radians(iAngle)),(width-width*0.505)*cos(radians(iAngle)),-(width-width*0.505)*sin(radians(iAngle)));
}
popMatrix();
}
void drawLine() {
pushMatrix();
strokeWeight(9);
stroke(30,250,60);
translate(width/2,height-height*0.074); // moves the starting coordinats to new location
line(0,0,(height-height*0.12)*cos(radians(iAngle)),-(height-height*0.12)*sin(radians(iAngle))); // draws the line according to the angle
popMatrix();
}
void drawText() { // draws the texts on the screen
pushMatrix();
if(iDistance>40) {
noObject = "Out of Range";
}
else {
noObject = "In Range";
}
fill(0,0,0);
noStroke();
rect(0, height-height*0.0648, width, height);
fill(98,245,31);
textSize(25);
text("10cm",width-width*0.3854,height-height*0.0833);
text("20cm",width-width*0.281,height-height*0.0833);
text("30cm",width-width*0.177,height-height*0.0833);
text("40cm",width-width*0.0729,height-height*0.0833);
textSize(40);
text("Pak Cyber Boy ", width-width*0.875, height-height*0.0277);
text("Angle: " + iAngle +" °", width-width*0.48, height-height*0.0277);
text("Distance: ", width-width*0.26, height-height*0.0277);
if(iDistance<40) {
text(" " + iDistance +" cm", width-width*0.225, height-height*0.0277);
}
textSize(25);
fill(98,245,60);
translate((width-width*0.4994)+width/2*cos(radians(30)),(height-height*0.0907)-width/2*sin(radians(30)));
rotate(-radians(-60));
text("30°",0,0);
resetMatrix();
translate((width-width*0.503)+width/2*cos(radians(60)),(height-height*0.0888)-width/2*sin(radians(60)));
rotate(-radians(-30));
text("60°",0,0);
resetMatrix();
translate((width-width*0.507)+width/2*cos(radians(90)),(height-height*0.0833)-width/2*sin(radians(90)));
rotate(radians(0));
text("90°",0,0);
resetMatrix();
translate(width-width*0.513+width/2*cos(radians(120)),(height-height*0.07129)-width/2*sin(radians(120)));
rotate(radians(-30));
text("120°",0,0);
resetMatrix();
translate((width-width*0.5104)+width/2*cos(radians(150)),(height-height*0.0574)-width/2*sin(radians(150)));
rotate(radians(-60));
text("150°",0,0);
popMatrix();
}