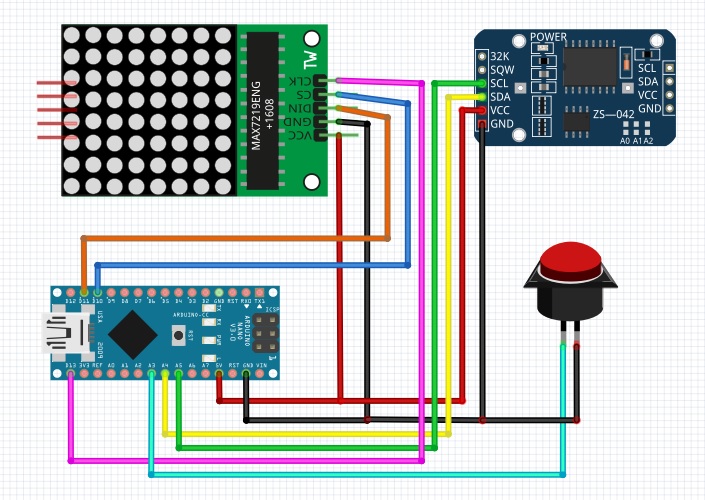
// Program to implement a Word Clock using the MD_MAX72XX library.
// by Marco Colli
//
// April 2016 - version 1.0
// - Initial release
//
// April 2017 - version 1.1
// - Added summer time auto adjustment (long press)
//
// June 2019 - version 1.2
// - Changed for new MD_MAX72xx library hardware definition
//
// Description:
// ------------
// The word clock 8x8 LED matrix module to shine light through a
// word mask printed on paper. The mask is placed over the matrix
// LEDs, folding over the small flaps on the sides and attaching them
// to the side of the matrix using double sided tape.
//
// The clock face (word matrix) for the clock can be found in the doc
// folder of this sketch (Microsoft Word document and PDF versions).
//
// Additional hardware required is RTC clock module (DS3231 used here)
// and a momentary-on switch (tact switch or similar).
//
// More information on the Word Clock can be found in the blog article at
// https://arduinoplusplus.wordpress.com/2016/04/24/max7219-led-matrix-module-mini-word-clock/
//
// Functions:
// ----------
// - To see the time in digits, press the mode switch once.
// - To set up the time:
// + Double click the mode switch
// + Then click to progress the hours
// + Double click to stop editing hours and edit minutes
// + Then click to progress the minutes
// + Double click to exit editing and set the new time
// Setup mode has a timeout for no inactivity. On exit it sets the new time
// and returns to normal word display.
//
// Library dependencies:
// ---------------------
// MD_DS1307 and MD_DS3231 RTC libraries found at https://github.com/MajicDesigns/DS1307
// and https://github.com/MajicDesigns/DS3231. Any other RTC may be
// substitiuted with few changes as the current time is passed to all
// matrix display functions.
//
// MD_MAX72xx library can be found at https://github.com/MajicDesigns/MD_MAX72XX
// MD_KeySwitch library is found at https://github.com/MajicDesigns/MD_KeySwitch
//
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Wire.h> // I2C library for RTC
#include <EEPROM.h> // for saving summer time status
#include <MD_MAX72xx.h>
#include <MD_KeySwitch.h>
#include <MD_DS3231.h>
// --------------------------------------
// Hardware definitions
// NOTE: For non-integrated SPI interface the pins will probably
// not work with your hardware and may need to be adapted.
const uint8_t CLK_PIN = 13; // (or SCK) connect to matrix CLK
const uint8_t DATA_PIN = 11; // (or MOSI) connect to matrix DATA
const uint8_t CS_PIN = 10; // (or SS) connect to matrix LOAD
const uint8_t MODE_SW_PIN = 3; // setup pin connected to mode switch
const uint8_t EE_SUMMER_FLAG = 0;
// --------------------------------------
// Miscelaneous defines
const uint8_t CLOCK_UPDATE_TIME = 5; // in seconds - time resolution to nearest 5 minutes does not need rapid updates!
const uint32_t SHOW_DELAY_TIME = 1000; // in millisecnds - how long to show time in digits
const uint32_t SETUP_TIMEOUT = 10000; // in milliseconds - timeout for setup mode
// --------------------------------------
// END OF USER CONFIGURABLE INFORMATION
// --------------------------------------
#define DEBUG 0
// --------------------------------------
// Enumerated types for state machines
typedef enum stateRun_t { SR_UPDATE, SR_IDLE, SR_SETUP, SR_TIME, SR_SUMMER_TIME };
typedef enum stateSetup_t { SS_DISP_HOUR, SS_HOUR, SS_DISP_MIN, SS_MIN, SS_END };
// --------------------------------------
// Global variables
MD_KeySwitch swMode(MODE_SW_PIN); // mode/setup switch handler
MD_MAX72XX clock = MD_MAX72XX(MD_MAX72XX::FC16_HW, CS_PIN, 1); // SPI hardware interface
//MD_MAX72XX clock = MD_MAX72XX(MD_MAX72XX::FC16_HW, DATA_PIN, CLK_PIN, CS_PIN, 1); // Arbitrary pins
#define ARRAY_SIZE(a) (sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]))
#if DEBUG
#define PRINT(s, x) { Serial.print(F(s)); Serial.print(x); }
#define PRINTS(x) Serial.print(F(x))
#define PRINTD(x) Serial.println(x, DEC)
#else
#define PRINT(s, x)
#define PRINTS(x)
#define PRINTD(x)
#endif
// --------------------------------------
// Font data used to set the time on the clock.
// The characters are 4 pixels wide so that 2 can fit on the display by shifting
// the data for the leftmost character and 'OR'ing in the rightmost character.
// Font data is stored in display rows.
const uint8_t FONT_ROWS = 8;
const PROGMEM uint8_t fontMap[][FONT_ROWS] =
{
{ 0x7, 0x5, 0x5, 0x5, 0x5, 0x5, 0x7, 0x0 }, // 0
{ 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x0 }, // 1
{ 0x7, 0x1, 0x1, 0x7, 0x4, 0x4, 0x7, 0x0 }, // 2
{ 0x7, 0x1, 0x1, 0x7, 0x1, 0x1, 0x7, 0x0 }, // 3
{ 0x4, 0x4, 0x5, 0x5, 0x7, 0x1, 0x1, 0x0 }, // 4
{ 0x7, 0x4, 0x4, 0x7, 0x1, 0x1, 0x7, 0x0 }, // 5
{ 0x7, 0x4, 0x4, 0x7, 0x5, 0x5, 0x7, 0x0 }, // 6
{ 0x7, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x0 }, // 7
{ 0x7, 0x5, 0x5, 0x7, 0x5, 0x5, 0x7, 0x0 }, // 8
{ 0x7, 0x5, 0x5, 0x7, 0x1, 0x1, 0x7, 0x0 }, // 9
{ 0x0, 0x0, 0x2, 0x7, 0x2, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0 }, // +
{ 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x7, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0 }, // -
};
// --------------------------------------
// Define the data for the words on the clock face.
// The clock face has the following letter matrix
// 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 <-- column
// A T W E N T Y D <-- row 0
// Q U A R T E R Y <-- row 1
// F I V E H A L F <-- row 2
// D P A S T O R O <-- row 3
// F I V E I G H T <-- row 4
// S I X T H R E E <-- row 5
// T W E L E V E N <-- row 6
// F O U R N I N E <-- row 7
//
// - Minutes to/past the hour are all in the rows 0-2 of the display.
// - Past/to text is on row 3
// - The hour name is in rows 4-7
//
// The words may be defined in one or more rows. So to define the bit
// pattern to illuminate for a word, just need to know the row number(s)
// and the bit pattern(s) to turn on for that row.
typedef struct clockWord_t
{
uint8_t row;
uint8_t data;
};
// Minutes and to/past are always on the same row, so they can be defined as
// individual elements.
const PROGMEM clockWord_t M_05 = { 2, 0b11110000 };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t M_10 = { 0, 0b01011000 };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t M_15 = { 1, 0b11111110 };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t M_20 = { 0, 0b01111110 };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t M_30 = { 2, 0b00001111 };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t TO = { 3, 0b00001100 };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t PAST = { 3, 0b01111000 };
// Some hour names are split across rows, so use more than one definition
// per word - make them all arrays for consistent handling in loop code.
//const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_01[] = { { 7, 0b01000011 } }; // 1-2 option
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_01[] = { { 7, 0b01001001 } }; // 1-1-1 symmetrical option
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_02[] = { { 6, 0b11000000 }, { 7, 0b01000000 } };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_03[] = { { 5, 0b00011111 } };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_04[] = { { 7, 0b11110000 } };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_05[] = { { 4, 0b11110000 } };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_06[] = { { 5, 0b11100000 } };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_07[] = { { 5, 0b10000000 }, { 6, 0b00001111 } };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_08[] = { { 4, 0b00011111 } };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_09[] = { { 7, 0b00001111 } };
//const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_10[] = { { 6, 0b10000011 } }; // 1-2 horizontal option
//const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_10[] = { { 6, 0b10001001 } }; // 1-1-1 horizontal option
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_10[] = { { 4, 0b00000001 }, { 5, 0b00000001 }, { 6, 0b00000001 } }; // vertical option
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_11[] = { { 6, 0b00111111 } };
const PROGMEM clockWord_t H_12[] = { { 6, 0b11110110 } };
// --------------------------------------
// Code
bool isSummerMode()
// Return true if summer mode is active
{
return(EEPROM.read(EE_SUMMER_FLAG) != 0);
}
uint8_t currentHour(uint8_t h)
// Change the RTC hour to include any summer time offset
// Clock always holds the 'real' time.
{
h += (isSummerMode() ? 1 : 0);
if (h > 12) h = 1;
return(h);
}
void dumpTime()
// Show displayed time to the debug display
{
uint8_t h = currentHour(RTC.h);
if (h < 10) PRINTS("0");
PRINT("", h);
PRINTS(":");
if (RTC.m < 10) PRINTS("0");
PRINT("", RTC.m);
PRINTS(":");
if (RTC.s < 10) PRINTS("0");
PRINT("", RTC.s);
PRINTS(" ");
}
void mapOffset(uint8_t *map, int8_t num)
// *map is a pointer to a FONT_ROWS byte buffer to capture the
// rows of the mapped number, num is the offset single digit
{
uint8_t sign = (num >= 0 ? 10 : 11); // 10th font char map is for a '+', the 11th for a '-'.
num = abs(num) % 10; // positive single digit
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < FONT_ROWS; i++)
{
*map = pgm_read_byte(&fontMap[sign][i]) << 4;
*map |= pgm_read_byte(&fontMap[num][i]);
map++;
}
}
void mapNumber(uint8_t *map, uint8_t num)
// *map is a pointer to a FONT_ROWS byte buffer to capture the
// rows of the mapped number, num is the decimal number to convert
{
uint8_t hi = num / 10;
uint8_t lo = num % 10;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < FONT_ROWS; i++)
{
*map = pgm_read_byte(&fontMap[hi][i]) << 4;
*map |= pgm_read_byte(&fontMap[lo][i]);
map++;
}
}
void mapShow(uint8_t *map)
// *map is a pointer to a FONT_ROWS byte buffer to display on the
// clock face.
{
clock.control(MD_MAX72XX::UPDATE, MD_MAX72XX::OFF);
clock.clear();
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < FONT_ROWS; i++)
clock.setRow(i, *map++);
clock.control(MD_MAX72XX::UPDATE, MD_MAX72XX::ON);
}
void setupTime(uint8_t &h, uint8_t &m)
// Handle the user interface to set the current time.
// Remains in this function until completed.
{
uint32_t timeLastActivity = millis();
uint8_t map[FONT_ROWS];
stateSetup_t state = SS_DISP_HOUR;
while (state != SS_END)
{
// check if we time out
if (millis() - timeLastActivity >= SETUP_TIMEOUT)
{
PRINTS("\nSetup inactivity timeout");
state = SS_END;
}
// process current state
switch (state)
{
case SS_DISP_HOUR: // show the hour
mapNumber(map, currentHour(RTC.h));
mapShow(map);
state = SS_HOUR;
break;
case SS_HOUR: // handle setting hours
switch (swMode.read())
{
case MD_KeySwitch::KS_DPRESS: // move on to minutes
timeLastActivity = millis();
state = SS_DISP_MIN;
break;
case MD_KeySwitch::KS_PRESS: // increment the hours
timeLastActivity = millis();
h++;
if (h == 13) h = 1;
state = SS_DISP_HOUR;
break;
}
break;
case SS_DISP_MIN: // show the minutes
mapNumber(map, m);
mapShow(map);
state = SS_MIN;
break;
case SS_MIN: // handle setting minutes
switch (swMode.read())
{
case MD_KeySwitch::KS_DPRESS: // move on to end
timeLastActivity = millis();
state = SS_END;
break;
case MD_KeySwitch::KS_PRESS: // increment the minutes
timeLastActivity = millis();
m = (m + 1) % 60;
state = SS_DISP_MIN;
mapShow(map);
break;
}
break;
default: // our work is done
state = SS_END;
}
}
}
void flipSummerMode(void)
// Reverse the the summer flag mode in the EEPROM
{
uint8_t map[FONT_ROWS];
// handle EEPROM changes
EEPROM.write(EE_SUMMER_FLAG, isSummerMode() ? 0 : 1);
PRINT("\nNew Summer Mode ", isSummerMode());
// now show the current offset on the display
mapOffset(map, (isSummerMode() ? 1 : 0));
mapShow(map);
delay(SHOW_DELAY_TIME);
}
void showTime(uint8_t h, uint8_t m)
// Display the current time in digits on the matrix.
// Remains in this function until completed.
{
uint8_t map[FONT_ROWS];
mapNumber(map, h);
mapShow(map);
delay(SHOW_DELAY_TIME);
mapNumber(map, m);
mapShow(map);
delay(SHOW_DELAY_TIME);
}
void updateClock(uint8_t h, uint8_t m)
// Work out what current time it is in words and turn on the right
// parts of the display. The time is passed to the function so that
// it is dependent of the time source.
// This logic tries to copy the approximations people make when reading
// analog time. It is consistent but arbitrary - note that any changes need
// to be made consistently across all the checks in this part of the code.
{
const uint8_t PRE_DELTA = 2; // minutes before the actual min
const uint8_t POST_DELTA = 2; // minutes after the actual min
const clockWord_t *H;
uint8_t numElements;
PRINTS("\nT: ");
dumpTime(); // debug output only
// freeze the clock display while we make changes to the matrix
clock.control(MD_MAX72XX::UPDATE, MD_MAX72XX::OFF);
clock.clear();
// minutes - are worked out in an interval [-PRE_DELTA, POST_DELTA] around the time
// to select the choice of words.
switch (m)
{
case 0 ... 0+POST_DELTA:
case 60-PRE_DELTA ... 59:
// nothing to say at top of the hour
break;
case 5-PRE_DELTA ... 5+POST_DELTA:
case 55-PRE_DELTA ... 55+POST_DELTA:
PRINTS("FIVE");
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&M_05.row), pgm_read_byte(&M_05.data));
break;
case 10-PRE_DELTA ... 10+POST_DELTA:
case 50-PRE_DELTA ... 50+POST_DELTA:
PRINTS("TEN");
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&M_10.row), pgm_read_byte(&M_10.data));
break;
case 15-PRE_DELTA ... 15+POST_DELTA:
case 45-PRE_DELTA ... 45+POST_DELTA:
PRINTS("QUARTER");
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&M_15.row), pgm_read_byte(&M_15.data));
break;
case 20-PRE_DELTA ... 20+POST_DELTA:
case 40-PRE_DELTA ... 40+POST_DELTA:
PRINTS("TWENTY");
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&M_20.row), pgm_read_byte(&M_20.data));
break;
case 25-PRE_DELTA ... 25+POST_DELTA:
case 35-PRE_DELTA ... 35+POST_DELTA:
PRINTS("TWENTY-FIVE");
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&M_05.row), pgm_read_byte(&M_05.data));
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&M_20.row), pgm_read_byte(&M_20.data));
break;
case 30-PRE_DELTA ... 30+POST_DELTA:
PRINTS("HALF");
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&M_30.row), pgm_read_byte(&M_30.data));
break;
}
// To/past display
if (m > 0+POST_DELTA && m < 60-PRE_DELTA) // top of the hour interval displays the hour only
{
if (m <= 30+POST_DELTA) // in the first half hour it is 'past' and ...
{
PRINTS(" PAST ");
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&PAST.row), pgm_read_byte(&PAST.data));
}
else // ... after the half hour it becomes 'to'
{
PRINTS(" TO ");
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&TO.row), pgm_read_byte(&TO.data));
}
}
// After the half hour we have also have to adjust the hour number!
if (m > 30 + POST_DELTA)
{
if (h < 12) h++;
else h = 1;
}
// hour - straight translation of nummber to data. However, the word can can
// span more than one line so the data is set up in arrays.
switch (currentHour(h))
{
case 1: H = H_01; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_01); PRINTS("ONE"); break;
case 2: H = H_02; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_02); PRINTS("TWO"); break;
case 3: H = H_03; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_03); PRINTS("THREE"); break;
case 4: H = H_04; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_04); PRINTS("FOUR"); break;
case 5: H = H_05; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_05); PRINTS("FIVE"); break;
case 6: H = H_06; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_06); PRINTS("SIX"); break;
case 7: H = H_07; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_07); PRINTS("SEVEN"); break;
case 8: H = H_08; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_08); PRINTS("EIGHT"); break;
case 9: H = H_09; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_09); PRINTS("NINE"); break;
case 10: H = H_10; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_10); PRINTS("TEN"); break;
case 11: H = H_11; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_11); PRINTS("ELEVEN"); break;
case 12: H = H_12; numElements = ARRAY_SIZE(H_12); PRINTS("TWELVE"); break;
}
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < numElements; i++)
clock.setRow(pgm_read_byte(&H[i].row), pgm_read_byte(&H[i].data));
// finally, update the display with new data
clock.control(MD_MAX72XX::UPDATE, MD_MAX72XX::ON);
}
void setup()
{
#if DEBUG
Serial.begin(115200);
#endif
PRINTS("\n[MD_MAX72XX_WordClock Demo]");
clock.begin();
clock.control(MD_MAX72XX::INTENSITY, 2 + (MAX_INTENSITY / 2));
swMode.begin();
swMode.enableRepeat(false);
// turn the clock on to 12H mode and make sure it is running
RTC.control(DS3231_12H, DS3231_ON);
RTC.control(DS3231_CLOCK_HALT, DS3231_OFF);
PRINT("\nSummer Mode ", isSummerMode());
}
void loop()
{
static stateRun_t state = SR_UPDATE;
static uint32_t timeLastUpdate = 0;
switch (state)
{
case SR_UPDATE: // update the display
timeLastUpdate = millis();
RTC.readTime();
updateClock(RTC.h, RTC.m);
state = SR_IDLE;
break;
case SR_IDLE: // wait for ...
// ... time to update the display or ...
if (millis() - timeLastUpdate >= CLOCK_UPDATE_TIME * 1000UL)
state = SR_UPDATE;
// ... user input from mode switch
switch (swMode.read())
{
case MD_KeySwitch::KS_DPRESS: state = SR_SETUP; break;
case MD_KeySwitch::KS_PRESS: state = SR_TIME; break;
case MD_KeySwitch::KS_LONGPRESS: state = SR_SUMMER_TIME; break;
}
break;
case SR_SETUP: // time setup
setupTime(RTC.h, RTC.m);
// write new time to the RTC
RTC.s = 0;
RTC.writeTime();
PRINTS("\nNew T: ");
dumpTime();
state = SR_UPDATE;
break;
case SR_TIME: // show time as digits
showTime(currentHour(RTC.h), RTC.m);
state = SR_UPDATE;
break;
case SR_SUMMER_TIME: // handle the summer time selection
flipSummerMode();
state = SR_UPDATE;
break;
default:
state = SR_UPDATE;
}
}